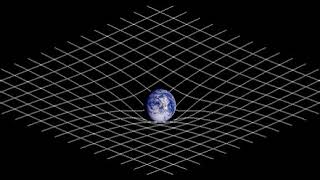
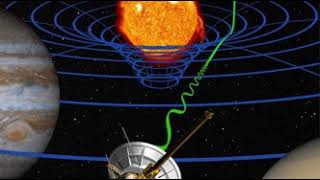
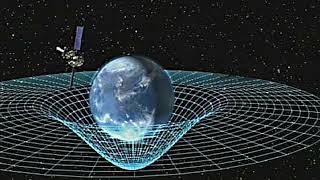
Space and time | Wikipedia audio article |

|
|
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
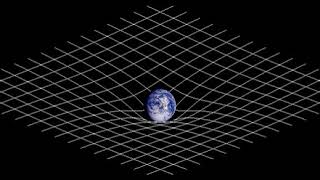
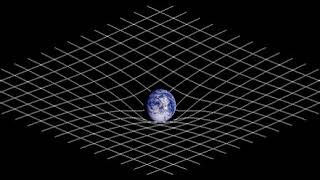
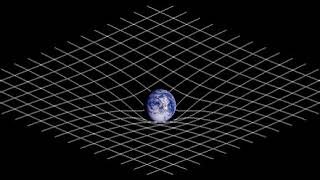
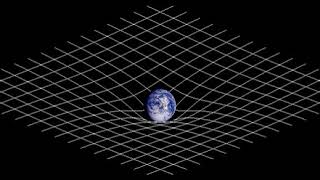
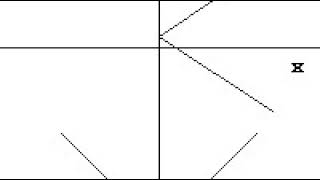
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spacetime 00:02:38 1 Introduction 00:02:47 1.1 Definitions 00:07:39 1.2 History 00:15:58 2 Spacetime in special relativity 00:16:09 2.1 Spacetime interval 00:25:48 2.2 Reference frames 00:26:46 2.3 Light cone 00:27:14 2.4 Relativity of simultaneity 00:27:30 2.5 Invariant hyperbola 00:28:26 2.6 Time dilation and length contraction 00:28:44 2.7 Mutual time dilation and the twin paradox 00:29:03 2.7.1 Mutual time dilation 00:29:09 2.7.2 Twin paradox 00:29:42 2.8 Gravitation 00:31:57 3 Basic mathematics of spacetime 00:32:38 3.1 Galilean transformations 00:33:45 3.2 Relativistic composition of velocities 00:35:03 3.3 Time dilation and length contraction revisited 00:37:53 3.4 Lorentz transformations 00:39:52 3.4.1 Deriving the Lorentz transformations 00:40:33 3.4.2 Linearity of the Lorentz transformations 00:40:44 3.5 Doppler effect 00:43:36 3.5.1 Longitudinal Doppler effect 00:48:26 3.5.2 Transverse Doppler effect 00:49:14 3.6 Energy and momentum 00:49:24 3.6.1 Extending momentum to four dimensions 00:50:21 3.6.2 Momentum of light 00:51:50 3.6.3 Mass-energy relationship 00:52:01 3.6.4 Four-momentum 00:52:13 3.7 Conservation laws 00:52:55 3.7.1 Total momentum 00:53:33 3.7.2 Choice of reference frames 00:53:49 3.7.3 Energy and momentum conservation 00:54:29 4 Beyond the basics 00:54:46 4.1 Rapidity 00:54:57 4.2 4‑vectors 00:56:12 4.2.1 Definition of 4-vectors 00:56:22 4.2.2 Properties of 4-vectors 00:57:45 4.2.3 Examples of 4-vectors 00:58:03 4.2.4 4-vectors and physical law 00:59:59 4.3 Acceleration 01:00:23 4.3.1 Dewan–Beran–Bell spaceship paradox 01:01:08 4.3.2 Accelerated observer with horizon 01:04:52 5 Introduction to curved spacetime 01:05:17 5.1 Basic propositions 01:05:56 5.2 Curvature of time 01:07:34 5.3 Curvature of space 01:07:50 5.4 Sources of spacetime curvature 01:08:10 5.4.1 Energy-momentum 01:08:26 5.4.2 Pressure and stress 01:09:36 5.4.3 Experimental verification 01:10:40 5.4.3.1 • Active, passive, and inertial mass 01:11:16 5.4.3.2 • Pressure as a gravitational source 01:11:22 5.4.3.3 • Gravitomagnetism 01:11:32 6 Technical topics 01:11:59 6.1 Is spacetime really curved? 01:14:00 6.2 Riemannian geometry 01:14:43 6.3 Curved manifolds 01:17:28 6.4 Privileged character of 3+1 spacetime 01:17:37 7 See also 01:18:48 8 Notes 01:19:20 9 Additional details 01:20:00 10 References 01:20:43 11 Further reading 01:20:58 12 External links 01:21:32 γmv approaches mv, the classical term for momentum. Following this perspective, γm can be interpreted as a relativistic generalization of m. Einstein proposed that the relativistic mass of an object increases with velocity according to the formula mrel 01:22:07 mrelc 01:25:00 ±pc. 01:25:04 Four-momentum 01:26:33 Conservation laws 01:27:21 Total momentum 01:28:19 m2v2 collide to produce a single particle of conserved mass m 01:28:38 (m1v1 + m2v2)/(m1 + m2). The total momentum p 01:29:53 Choice of reference frames 01:30:48 Energy and momentum conservation 01:31:08 v − u, the momentum p' 01:31:33 0 both before and after collision. In the Newtonian analysis, conservation of mass dictates that m 01:32:25 mv, fail to behave properly under Lorentzian transformation. The linear transformation of velocities v' 01:35:00 4.12 MeV. Most of the energy is carried off by the near-zero-mass neutrino. 01:35:08 Beyond the basics 01:35:18 The topics in this section are of significantly greater technical difficulty than those in the preceding sections and are not essential for understanding Introduction to curved spacetime. 01:35:31 Rapidity 01:39:17 {\displaystyle \beta 01:43:06 4‑vectors 01:44:23 Definition of 4-vectors 01:46:17 Properties of 4-vectors 01:49:58 Examples of 4-vectors 01:56:18 4-vectors and physical law 01:57:15 Acceleration 01:58:12 Dewan–Beran–Bell spaceship paradox 02:03:07 Accelerated observer with horizon 02:05:43 {\displaystyle \gamma 02:08:30 Introduction to curved spacetime 02:08:40 Basic propositions 02:12:02 GMmg /r2 02:13:07 Curvature of time 02:14:17 (2gh)1/2, so that its total energy E, as measured by an observer on the ground, is m + ½mv2/c2 02:14:53 m', since otherwise one would be able to construct a perpetual motion device. We therefore predict that E' 02:18:36 Curvature of space 02:25:03 Sources of spacetime curvature 02:26:47 j terms (green) represent isotropic pressure, and the i ≠ j terms (blue) represent shear stresses.One important conclusion to be derived from the equations is that, colloquially speaking, gravity itself creates gravity. Energy has mass. Even in Newtonian gravity, the gravitational field is associated with an energy, E 02:27:47 Energy-momentum 02:29:32 Pressure and stress 02:30:43 Experimental verification 02:31:36 • Active, passive, and inertial mass 02:34:00 • Pressure as a gravitational source 02:35:52 9, while bromine has Z 02:36:59 • Gravitomagnetism 02:38:30 Technical topics 02:38:40 Is spacetime ... |