Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Heart Surgery PreOp® Patient Education Medical video |

|
|
https://preop.com & http://PostCare.com
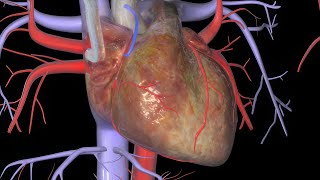
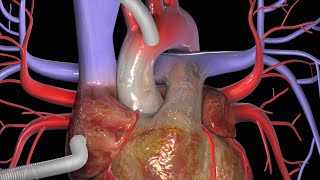
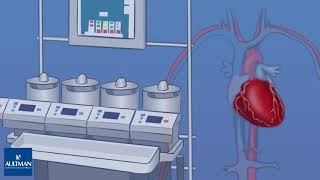
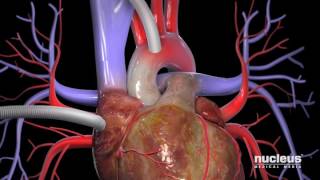
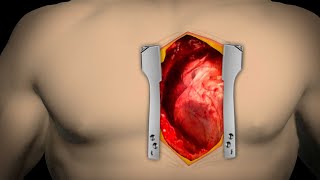
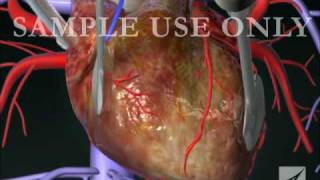
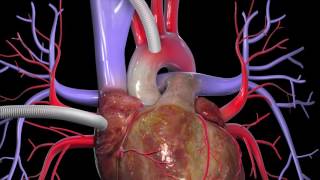
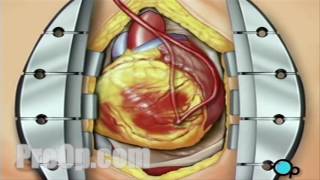
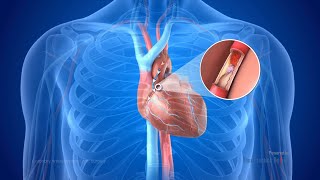
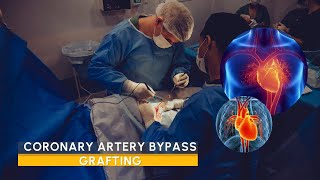
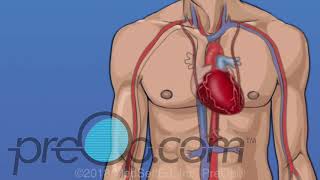
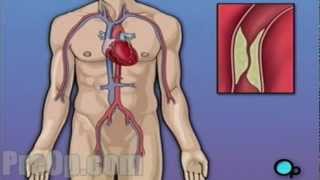
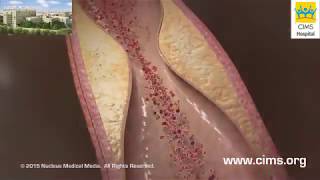
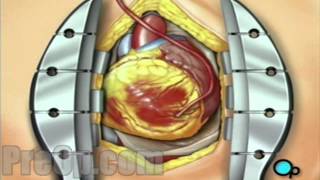
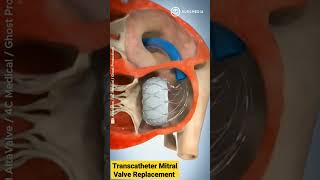
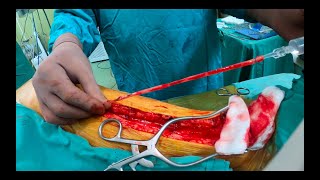
Patient Education Company Your doctor has recommended that you have coronary artery bypass surgery. But what does that actually mean? Your heart is located in the center of your chest. It is surrounded by your rib cage and protected by your breastbone. Your heart's job is to keep blood continually circulating throughout your body. The vessels that supply the body with oxygen-rich blood are called arteries. The vessels that return blood to the heart are called veins. Like any other muscle in the body, the heart depends on a steady supply of oxygen rich blood. The arteries that carry this blood supply to the heart muscle are called coronary arteries. Sometimes, these blood vessels can narrow or become blocked by deposits of fat, cholesterol and other substances collectively known as plaque. Over time, plaque deposits can narrow the vessels so much that normal blood flow is restricted. In some cases, the coronary artery becomes so narrow that the heart muscle itself is in danger. Coronary bypass surgery attempts to correct this serious problem. In order to restore normal blood flow, the surgeon removes a portion of a blood vessel from the patient's leg or chest, most probably the left internal mammary artery and the saphenous vein. Your doctor uses one or both of these vessels to bypass the old, diseased coronary artery and to build a new pathway for blood to reach the heart muscle. These transplanted vessels are called grafts and depending on your condition, your doctor may need to perform more than one coronary artery bypass graft. Of course, operating on the heart is a complex and delicate process and in the case of bypass surgery, your doctor will most likely need to stop your heart before installing the graft. During the time that your heart is not beating, a special machine, called a heart-lung machine, will take over the job of circulating and oxygenating your blood. By using this machine, your doctor is able to repair the heart without interfering with the blood flow to the rest of the body. Following surgery, your heart will be restarted and you will be disconnected from the heart-lung machine. On the day of your operation, you will be asked to put on a surgical gown. You may receive a sedative by mouth and an intravenous line may be put in. You will then be transferred to an operating table. The anesthesiologist will begin to administer anesthesia - most probably general anesthesia by injection and inhalation mask. The surgeon will then apply an antiseptic solution to the skin and place a sterile drape around the operative site. One or more sections of blood vessel will be taken from the leg, thigh or chest wall and the incision at those points will be sutured and bandaged. Then, your doctor will make a vertical incision in the center of the chest. Skin and other tissue will be pulled back in order to expose the breast bone. Your doctor will carefully divide the breast bone and a special instrument called a retractor will be used to hold the chest open. Once your doctor has a clear view of the heart, he or she will make an incision in the pericardium - a thin membrane that encloses the heart. Pulling the pericardium back will reveal the beating heart. Before the graft vessel or vessels can be attached, a heart-lung machine must be connected, A heart lung machine takes over the job of circulating and oxygenating the blood so that your doctor will be free to stop your heart for the length of the operation. To connect the heart-lung machine, one tube is placed into the aorta and a second tube is placed into the right atrium of the heart. One or two smaller tubes are then inserted into the heart. These will carry a special solution that helps preserve the hearts temperature. When all the tubes are in place, the surgical team will turn on the bypass machine. It will begin to circulate the blood as the heart cools. When the temperature of the heart muscle has reached the proper level, a clamp is placed on the aorta. At that point, blood will no longer flow through the heart and it can be safely stopped and repaired. To complete the bypass graft procedure, your doctor attaches the ends of the new vessels on either side of the diseased area or areas of the old coronary artery. Once the grafts have been completed, the clamp on the aorta is removed and the heart is allowed to begin beating again. As the temperature and the rhythm of the heart slowly return to normal, the heart-lung machine is disconnected. The pericardium can now be closed over the heart. Your doctor will position two special drainage tubes in the chest cavity. These tubes prevent fluid from building up around the heart during the healing process. The breast bone is then closed with metal wire and the remaining tissue is closed with sutures. Finally a sterile bandage is applied. Patient Education Company |