Types of Immunity/Active and Passive Immunity |

|
|
#sowmyanagaraj #sowmyanrao #swiminscience
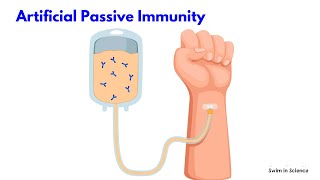
Types of immunity There are mainly two types of immunity. They are, active immunity and passive immunity Active Immunity: Active immunity is defined as the immunity that is generated following exposure to a pathogen. It is long-lasting, and sometimes life-long. Active immunity can be either natural or artificial. Natural active immunity occurs when a person is infected by a pathogen. For example, if a person is infected with the chickenpox virus, the person’s body fights against the virus and also develops immune memory for the virus. If the person is exposed to the same virus in the future, he will be able to fight against it quickly without developing the disease. In other words, the person becomes immune to chickenpox disease in the future. Artificial active immunity is the immunity developed by a person against a disease following vaccination. Vaccines are weakened or dead form of a pathogen that is known to stimulate an immune response without causing infection. An example is, vaccination against coronavirus allows the body to recognize and fight against covid without causing any symptoms or with mild symptoms. Passive Immunity: Passive immunity is protection from a disease provided by antibodies created outside of the individual’s body. Passive immunity provides protection immediately. However, it is short-lived as the received person cannot replenish the antibodies continuously. Passive immunity can be either natural or artificial. Natural passive immunity is when a person receives antibodies to a pathogen that have not been generated by their own immune system by natural means rather than medical intervention. This typically refers to the passage of antibodies from mother to baby across the placenta which is also called maternal passive immunity. These antibodies can protect the womb from infections. After birth, an infant continues to receive passive immunity to disease from antibodies found in breast milk, especially colostrum, the protein-rich milk produced in the first few days following birth. Maternal passive immunity is important for protecting infants until their own immune system is mature enough to protect them. Artificial passive immunity is conferred by the injection of antibodies generated by a different person or animal, or artificially in the laboratory, into an individual. These antibody-containing preparations are termed antisera and are used as a therapeutic treatment when there is a risk of some infections. Following a bite from a potentially rabies-infected animal, when a baby is born to a Hepatitis B-positive mother or following a bite from a venomous snake, the appropriate antisera or antivenom may be administered to offer passive immunity. References Kelly, J., 1992. Immunology: by Janis Kuby, WH Freeman. https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/active-vs-passive-immunity-differences-and-definition-335112 https://www.healthkart.com/connect/difference-between-natural-immunity-and-artificial-immunity/ https://www.chop.edu/centers-programs/vaccine-education-center/human-immune-system/types-immunity |