Behavioural genetics | Wikipedia audio article |

|
|
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
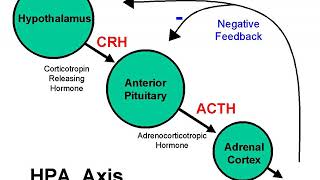
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Behavioural_genetics 00:02:05 1 History 00:06:23 2 Methods 00:06:50 2.1 Animal studies 00:08:10 2.2 Twin and family studies 00:15:28 2.3 Measured genetic variants 00:18:32 2.4 Quasi-experimental designs 00:20:51 3 General findings 00:22:53 3.1 Genetic influences on behaviour are pervasive 00:24:48 3.2 Nature of environmental influence 00:29:28 3.3 Nature of genetic influence 00:33:55 4 Criticisms and controversies Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago. Learning by listening is a great way to: - increases imagination and understanding - improves your listening skills - improves your own spoken accent - learn while on the move - reduce eye strain Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone. Listen on Google Assistant through Extra Audio: https://assistant.google.com/services/invoke/uid/0000001a130b3f91 Other Wikipedia audio articles at: https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=wikipedia+tts Upload your own Wikipedia articles through: https://github.com/nodef/wikipedia-tts Speaking Rate: 0.9482057725019902 Voice name: en-US-Wavenet-B "I cannot teach anybody anything, I can only make them think." - Socrates SUMMARY ======= Behavioural genetics, also referred to as behaviour genetics, is a field of scientific research that uses genetic methods to investigate the nature and origins of individual differences in behaviour. While the name "behavioural genetics" connotes a focus on genetic influences, the field broadly investigates genetic and environmental influences, using research designs that allow removal of the confounding of genes and environment. Behavioural genetics was founded as a scientific discipline by Francis Galton in the late 19th century, only to be discredited through association with eugenics movements before and during World War II. In the latter half of the 20th century, the field saw renewed prominence with research on inheritance of behaviour and mental illness in humans (typically using twin and family studies), as well as research on genetically informative model organisms through selective breeding and crosses. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, technological advances in molecular genetics made it possible to measure and modify the genome directly. This led to major advances in model organism research (e.g., knockout mice) and in human studies (e.g., genome-wide association studies), leading to new scientific discoveries. Findings from behavioural genetic research have broadly impacted modern understanding of the role of genetic and environmental influences on behaviour. These include evidence that nearly all researched behaviors are under a significant degree of genetic influence, and that influence tends to increase as individuals develop into adulthood. Further, most researched human behaviours are influenced by a very large number of genes and the individual effects of these genes are very small. Environmental influences also play a strong role, but they tend to make family members more different from one another, not more similar. |