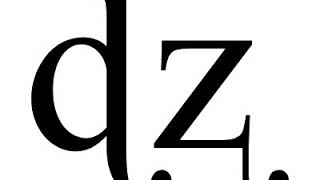Voice (phonetics) | Wikipedia audio article |

|
|
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
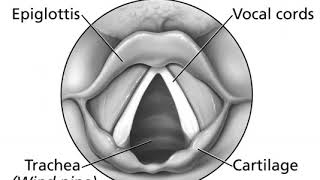
Voice (phonetics) 00:01:45 1 Notation 00:02:54 2 In English 00:06:31 3 Degrees of voicing 00:07:36 4 Voice and tenseness 00:08:26 5 See also Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago. Learning by listening is a great way to: - increases imagination and understanding - improves your listening skills - improves your own spoken accent - learn while on the move - reduce eye strain Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone. You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCuKfABj2eGyjH3ntPxp4YeQ You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through: https://github.com/nodef/wikipedia-tts "The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing." - Socrates SUMMARY ======= Voice is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants). It is also called "voicing". Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (also called unvoiced) or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts: Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal folds vibrate, its primary use in phonetics to describe phones, which are particular speech sounds. It can also refer to a classification of speech sounds that tend to be associated with vocal cord vibration but may not actually be voiced at the articulatory level. That is the term's primary use in phonology: to describe phonemes; while in phonetics its primary use is to describe phones.At the articulatory level, a voiced sound is one in which the vocal folds vibrate, and a voiceless sound is one in which they do not. For example, voicing accounts for the difference between the pair of sounds associated with the English letters "s" and "z". The two sounds are transcribed as [s] and [z] to distinguish them from the English letters, which have several possible pronunciations, depending on the context. If one places the fingers on the voice box (i.e. the location of the Adam's apple in the upper throat), one can feel a vibration while zzzz is pronounced but not with ssss. (For a more detailed, technical explanation, see modal voice and phonation.) In most European languages, with a notable exception being Icelandic, vowels and other sonorants (consonants such as m, n, l, and r) are modally voiced. When used to classify speech sounds, voiced and unvoiced are merely labels used to group phones and phonemes together for the purposes of classification. |