Pavlov's Dog experiment | Classical conditioning theory | Respondent conditioning |

|
|
#Pavlov #classicalconditioning #behaviourism #CTET #TET #Pavlovdogexperiment
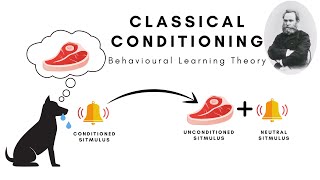
Classical conditioning is learning through association and was discovered by Russian physiologist Pavlov. In simple terms, two stimuli are linked together to produce a new learned response in a person or animal. If you pair a neutral stimulus (NS) with an unconditioned stimulus (US) that already triggers an unconditioned response (UR) that neutral stimulus will become a conditioned stimulus (CS), triggering a conditioned response (CR) similar to the original unconditioned response. There are three stages of classical conditioning. Stage 1: Before Conditioning: at this stage, unconditioned stimulus (UCS) produces an unconditioned response (UCR) in subject Stage 2: During Conditioning: During this stage, neutral stimulus (NS) is associated with the unconditioned stimulus (UCS), it now becomes conditioned stimulus (CS). Stage 3: After Conditioning: Now the conditioned stimulus (CS) has been associated with the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) to create a new conditioned response (CR), which is similar to the response generated by an unconditioned stimulus (UCS). Example of classical conditioning: Pavlov's experiment with dogs The most famous example of classical conditioning was Ivan Pavlov's experiment with dogs, who salivated in response to a bell tone. Pavlov showed that when a bell was sounded each time the dog was fed, the dog learned to associate the sound with the presentation of the food. Credit: https://www.simplypsychology.org/behaviorism.html https://www.simplypsychology.org/pavlov.html a href="https://www.freepik.com/free-vector/pavlov-s-dog-experiment-vector_39265134.htm#query=pavlov&position=0&from_view=search&track=sph"Image by brgfxa on Freepik |