What is Carbon Nanotube and It's Properties and Applications |

|
|
CARBON NANOTUBES:
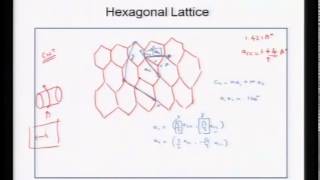
“Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are tubes made of carbon with diameters characteristically measured in nanometers” or “Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are allotropes of carbon with a nanostructure that have a length-to-diameter ratio greater than 1,000,000” History: A new form of carbon, Buckminster fullerene (C_60), was discovered in 1985 by a team headed by Korto and coworkers. Besides diamond, graphite, and fullerene. One dimensional nanotube is another form of carbon first reported by Ijima who inspired the world with his discovery of new carbon nanotube materials in 1991. How to fabricate Carbon Nanotubes? Techniques have been developed to produce nanotubes in sizable quantities, including: Arc discharge Laser ablation Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) High-pressure carbon monoxide disproportionation (HiPCO) whereas CVD is popular among all of them. Classification of Carbon Nanotubes: Carbon nanotubes are classified in following two types: SWCNTs : Single-walled carbon nanotubes MWCNTs Multiple-walled carbon nanotubes. Comparison between SWCNT and MWCNT: A MWCNT is a stack of graphene sheets rolled up into concentric cylinders. Each nanotube is a single molecule composed of millions of atoms and the length of this molecule can be tens of micrometers long with diameters as small as 0.7 nm. The SWCNTs usually contain only 10 atoms around the circumference and the thickness of the tube is only one-atom thick. MWCNTs are larger and consist of many single-walled tubes stacked one inside the other. The name MWCNT is restricted to nanostructures with outer diameter of less than 15 nm, above which the structures are called carbon nanofibers. CNTs are different from carbon fibers, which are not single molecules but strands of layered-graphite sheet. Types of CNTs: There are two different basic structures but there are three different possible types of carbon nanotubes which are stated below: Armchair carbon nanotubes Zigzag carbon nanotubes Chiral carbon nanotubes The difference in these types of carbon nanotubes are shaped depending on how the graphite is “rolled up” during its formation process. The choice of rolling axis comparative to the hexagonal network of the graphene sheet and the radius of the closing cylinder allows for diverse types of SWCNTs. Properties: Carbon-Carbon bonds give carbon nanotubes astonishing mechanical properties. No previous material has displayed the combination of excellent mechanical, thermal, and electronic properties. Carbon nanotubes are the strongest materials ever discovered by mankind. The highest measured tensile strength or breaking strain for a carbon nanotube was up to 63 GPa which is around 50 times higher than steel. The electronic properties of carbon nanotubes are also extraordinary having high electrical conductivity (comparable to copper). The most astounding fact is that nanotubes can be metallic or semiconducting. CNTs have good chemical and environmental stability and high thermal conductivity (~3000 W/m/K, comparable to diamond). Application: Due to their high strength, low weight, and flexibility CNTS can do wonders. Following are some applications of carbon nanotubes. CNT production is also used in bulk composite materials and thin films. Used in aerospace Energy storage devices can be manufactured In drug delivery In medicine Biotechnology field Can be used to fabricate nanocomposites Manufacturing of transistors |