MPEG-4 Part 2 | Wikipedia audio article |

|
|
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
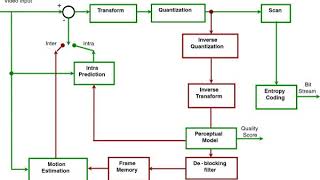
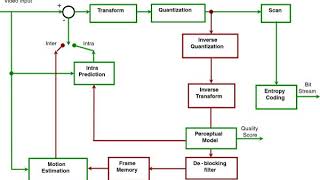
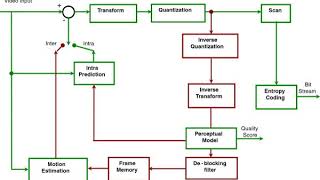
MPEG-4 Part 2 Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago. Learning by listening is a great way to: - increases imagination and understanding - improves your listening skills - improves your own spoken accent - learn while on the move - reduce eye strain Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone. You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCuKfABj2eGyjH3ntPxp4YeQ You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through: https://github.com/nodef/wikipedia-tts "The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing." - Socrates SUMMARY ======= MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally ISO/IEC 14496-2) is a video compression format developed by MPEG. It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It is a discrete cosine transform compression standard, similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Several popular codecs including DivX, Xvid and Nero Digital implement this standard. Note that MPEG-4 Part 10 defines a different format from MPEG-4 Part 2 and should not be confused with it. MPEG-4 Part 10 is commonly referred to as H.264 or AVC, and was jointly developed by ITU-T and MPEG. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functionality video object layer, the video object layer with short headers (which provides bitstream compatibility with base-line H.263). MPEG-4 Part 2 is partially based on ITU-T H.263. The first MPEG-4 Video Verification Model (simulation and test model) used ITU-T H.263 coding tools together with shape coding. |