Electroconvulsive Therapy ECT (The Truth) |

|
|
The truth about electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
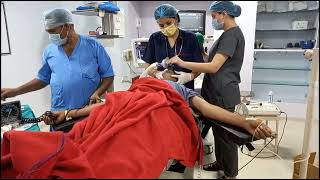
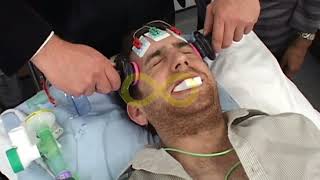
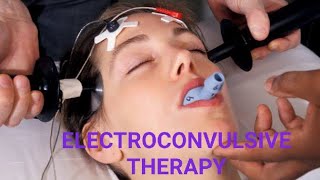
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders.[1] Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passed through the brain, for 100 milliseconds to 6 seconds duration, either from temple to temple (bilateral ECT) or from front to back of one side of the head (unilateral ECT). The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti[2] and rapidly replaced less safe and effective forms of biological treatments in use at the time. ECT is often used with informed consent[3] as a safe and effective intervention for major depressive disorder, mania, and catatonia.[4] ECT machines were originally placed in the Class III category by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1976.[5] They were re-classified as Class II devices, for treatment of catatonia, major depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder, in 2018.[6] Aside from effects on the brain, the general physical risks of ECT are similar to those of brief general anesthesia.[7]: 259 Immediately following treatment, the most common adverse effects are confusion and transient memory loss.[4][8] Among treatments for severely depressed pregnant women, ECT is one of the least harmful to the fetus.[9] A usual course of ECT involves multiple administrations, typically given two or three times per week until the patient is no longer suffering symptoms. ECT is administered under anesthesia with a muscle relaxant.[10] ECT can differ in its application in three ways: electrode placement, treatment frequency, and the electrical waveform of the stimulus. These treatment parameters can pose significant differences in both adverse side effects and symptom remission in the treated patient. Placement can be bilateral, where the electric current is passed from one side of the brain to the other, or unilateral, in which the current is solely passed across one hemisphere of the brain. High-dose unilateral ECT has some cognitive advantages compared to moderate-dose bilateral ECT while showing no difference in antidepressant efficacy.[11] ECT appears to work in the short term via an anticonvulsant effect primarily in the frontal lobes and longer term via neurotrophic effects primarily in the medial temporal lobe. In 1982, a young nurse was suffering from severe, unrelenting depression. She couldn’t work, socialize or concentrate. One controversial treatment changed everything: after two courses of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) her symptoms lifted. So what exactly is electroconvulsive therapy and why is it so stigmatized? Helen M. Farrell details the history and evolution of ECT. Lesson by Helen Farrell, directed by Artrake Studio. Thank you so much to our patrons for your support! Without you this video would not be possible! Dan Paterniti, Jerome Froelich, Tyler Yoshizumi, Martin Stephen, Justin Carpani, Faiza Imtiaz, Khalifa Alhulail, Tejas Dc, Benjamin & Shannon Pinder, Srikote Naewchampa, Sage Curie, Exal Enrique Cisneros Tuch, Ana Maria, Vignan Velivela, Ahmad Hyari, eden sher, Travis Wehrman, Louisa Lee, Kiara Taylor, Аркадий Скайуокер, Milad Mostafavi, Rob Johnson, Clarence E. Harper Jr., Mihail Radu Pantilimon, Karthik Cherala, haventfiguredout , Violeta Cervantes, Elaine Fitzpatrick, Lyn-z Schulte, cnorahs , Henrique 'Sorín' Cassús, Tim Robinson, Jun Cai, Joichiro Yamada, Paul Schneider, Amber Wood, Ophelia Gibson Best, Cas Jamieson, Michelle Stevens-Stanford, Phyllis Dubrow, Andreas Voltios, Eunsun Kim, Philippe Spoden, Samantha Chow, Ayala Ron, Manognya Chakrapani, Simon Holst Ravn, Doreen Reynolds-Consolati, Rakshit Kothari and Melissa Sorrells. #ECT #Electroconvulsive_Therapy |