Three Kingdoms | Wikipedia audio article |

|
|
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
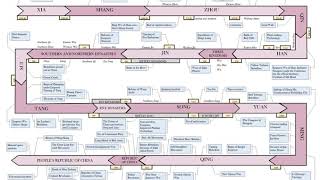
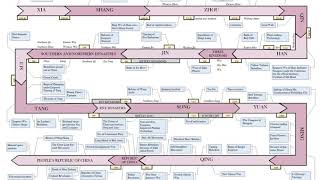
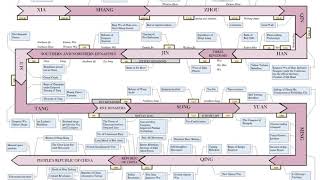
Three Kingdoms Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago. Learning by listening is a great way to: - increases imagination and understanding - improves your listening skills - improves your own spoken accent - learn while on the move - reduce eye strain Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone. You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCuKfABj2eGyjH3ntPxp4YeQ You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through: https://github.com/nodef/wikipedia-tts "The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing." - Socrates SUMMARY ======= The Three Kingdoms (220–280) was the tripartite division of China between the states of Wei (魏), Shu (蜀), and Wu (吳). It started with the end of the Han dynasty and was followed by the Jin dynasty. The term "Three Kingdoms" is something of a misnomer, since each state was eventually headed not by a king, but by an emperor who claimed suzerainty over all China. Nevertheless, the term "Three Kingdoms" has become standard among sinologists. To further distinguish the three states from other historical Chinese states of similar names, historians have added a relevant character: Wei is also known as Cao Wei (曹魏), Shu is also known as Shu Han (蜀漢), and Wu is also known as Dong (or Eastern) Wu (東吳). Academically, the period of the Three Kingdoms refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in AD 220 and the conquest of the state of Wu by the Jin dynasty in 280. The earlier, "unofficial" part of the period, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting between warlords in various parts of China. The middle part of the period, from 220 to 263, was marked by a more militarily stable arrangement between three rival states of Wei, Shu, and Wu. The later part of the era was marked by the conquest of Shu by Wei (263), the usurpation of Wei by the Jin dynasty (266), and the conquest of Wu by the Jin (280). The Three Kingdoms period is one of the bloodiest in Chinese history. A nationwide census taken in AD 280, following the reunification of the Three Kingdoms under the Jin shows a total of 2,459,840 households and 16,163,863 individuals which was only a fraction of the 10,677,960 households, and 56,486,856 individuals reported during the Han era. While the census may not have been particularly accurate due to a multitude of factors of the times, the Jin in AD 280 did make an attempt to account for all individuals where they could.Technology advanced significantly during this period. Shu chancellor Zhuge Liang invented the wooden ox, suggested to be an early form of the wheelbarrow, and improved on the repeating crossbow. Wei mechanical engineer Ma Jun is considered by many to be the equal of his predecessor Zhang Heng. He invented a hydraulic-powered, mechanical puppet theatre designed for Emperor Ming of Wei, square-pallet chain pumps for irrigation of gardens in Luoyang, and the ingenious design of the south-pointing chariot, a non-magnetic directional compass operated by differential gears.Although relatively short, this historical period has been greatly romanticized in the cultures of China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. It has been celebrated and popularized in operas, folk stories, novels and in more recent times, films, television, and video games. The best known of these is Luo Guanzhong's Romance of the Three Kingdoms, a Ming dynasty historical novel based on events in the Three Kingdoms period. The authoritative historical record of the era is Chen Shou's Records of the Three Kingdoms, along with Pei Songzhi's later annotations of the text. |